What is product localization?
Product localization is the process of adapting your product or service to a new target audience’s language, culture, and commercial environment, typically when entering a new country or region.
This process allows your organization to become more competitive in global markets, as you can tailor your product to meet the needs and expectations of a diverse customer base.
The key to the localization process is ensuring the product feels like it was designed for that audience, rather than feeling like an adapted or translated version.
Localization vs translation
Product localization is more than simply translating copy and launching in a new region. Successful localization requires strategically adapting your product to fit your new target audience. This includes modifying:
- Packaging,
- User interface,
- Manuals,
- Customer service,
- Messaging,
- Colour choices,
- Marketing activity,
- Seasonal promotions,
- And much more.
Your company will also need to consider legal and regulatory requirements and how those differ from the product’s country of origin.

Benefits of product localization
There are so many reasons to ensure your product is localized before launching in a new region – here are some of the main ones:
- Compete with local and international brands
- Increase total addressable market (TAM)
- Quickly grow your customer base
- Create brand loyalty and trust
- More effective go-to-market (GTM) strategy
- Faster time to market
- Higher revenue and profits
Approaches to localization
There are a few different ways your team can approach localization. Some opt to wait until everything is meticulously translated, while others choose to translate in sprints and launch as they go.
Let’s discuss your options so you can select the right approach for your org.
Waterfall
The waterfall approach is the more traditional method of localization. This approach involves translating and adjusting all content and features before launching the product into the new market.
Essentially, this is a slow and steady process, allowing you to launch a ready-to-go product that’s been vetted and fully localized for your audience. However, this can be time-consuming and expensive, as you have to wait on each element to be ready before generating revenue from your efforts.
With this in mind, it’s important to start this process early in product development so you have enough time to complete the translations and ensure they’re up to scratch.
Agile
To speed up the time it takes to get your product to market, you can take the agile approach to localization. This method involves translating and adjusting your product in short sprints, then releasing that batch.
This means you can launch your MVP quicker, then add additional features as they’re translated and ready to launch. Often this approach aligns more closely with how product managers and developers operate.
Plus, you’ll be able to adapt to changes in the market environment and stay flexible when challenges arise.
However, it’s important to have a robust process in place to ensure content is translated consistently throughout this process – you can do this by using a localization tool.
Continuous
And finally, you can choose a continuous approach to localization. This involves translating all content as soon as it’s created, allowing your product to always be available in all regions.
This prevents any waiting time for release as translation is built into your product development processes. However, it does require excellent project management to ensure everything runs smoothly as tasks are passed between the product and localization teams.

Types of product localization
Linguistic
Linguistic localization involves translating the content within your product. But it goes beyond directly translating every word – it’s about translating the meaning to a new audience.
This includes adjusting phrases, expressions, and idioms to local variations to ensure audiences still understand your core message. It’s also important to check the sentiment or cultural meaning behind words and phrases to ensure you’re making the right impression.
Cultural
Speaking of cultural differences, it’s also important to adjust your product and marketing to meet the expectations of your customers in different markets.
For example, you may need to change your models and their clothing choices when launching ads in different countries to better meet expectations.
It’s also important to recognise differences in visual understanding and shared knowledge. Colors, images, and traditions can differ widely across cultures, so it’s important to take note so you can build trust (rather than offend).
Hardware and software
While it may seem basic, it’s important to ensure your hardware and software are adjusted to the region you’re entering. This includes adapting plugs, ensuring operating systems make sense, and adapting the user interface to meet expectations.
For example, how responsive your audience expects your product to be may depend on the region you’re entering.
Another key element we’ll discuss in more detail later is ensuring your user interface can support double-byte languages, languages with complex scripts, and right-to-left languages.
Customer support
Finally, it’s necessary to localize customer support for the region. This involves providing support in the local language and hiring native customer service reps – you could even set up local locations to provide support.
You can also create a social media presence in the target language, creating another place to support and build trust with users.

7 steps to create a product localization strategy
1. Market research
First things first, you have to understand the market and audience you’re going into. This involves conducting market research into your competition in the region, the regulations your business may face, and the preferences of your potential customers.
Cultural and social differences in a region may change the level of competition you’re up against; for example, how likely your customers are to shop at small, local businesses will determine if they are a threat.
If you can, interview some potential customers in this area to understand their thoughts on your existing product and how it compares to what they’re used to – this will serve as a great starting point when localizing your product.
2. Set goals, budget, and timeline
Localization is time-consuming and expensive, so don’t just blindly get started. Take some time to consider why you’re undertaking this project.
What’s the goal of your localization project? Which specific results are you looking to achieve? By when?
Whether you’re looking to double revenue in the next year or increase your user base by 20% by Q4, setting a goal helps to ground your project and allows you to make better decisions.
It’s also important to set a budget and timeline for your project to ensure you launch on time and don’t run out of funds.
3. Internationalization
Next, it’s time to set up your product for success by ensuring it has multi-language support built into its foundational code.
In short, this means:
- Using the correct text encoding standard, such as UTF-8
- Making your product Unicode aware – this allows support for right-to-left languages, double-byte languages, and languages with complex scripts.
- Avoiding hard-coded text where possible
- When not possible, choose a framework for exporting hard-coded string identifiers to make translation easier
- Minimize the use of strings that are linked together to avoid complications during translation
- Keep your design flexible to allow different date and time formats, currencies, and scripts
Ensuring you take these steps early in product development allows for a much smoother localization process, as you won’t need to re-code your software to add translations.

4. Create a translation toolkit
Once your product is set up and ready for translation, you can start to build a translation toolkit to assist your localization team. This should include all the information your translation team will need to complete their tasks.
Such as:
- Project guidelines
- Project timeline
- Product or industry-specific translation glossaries
- Tone of voice guides
- User persona information
- Any limitations, such as character count
- Screenshots, images, or diagrams showing the user interface
This toolkit may also include creating a translation library to speed up translation by – you guessed it – reusing translations.
5. Translate and build your localized product
Once the translation toolkit has been built and passed on to your localization team, they can start translating your product copy into the required language.
After the translation process is complete, it should be proofed and signed off before your product team starts building the localized product with the new copy.
6. Testing and quality assurance
Before you release your newly localized product, it should be rigorously tested to ensure it works as intended and makes sense to your new customers.
Start by beta testing your software to ensure there are no bugs from translating the text. One out-of-place heading or incorrect paragraph will look broken, immediately reducing trust with your new users.
Once all bugs are fixed, you’ll want to ensure the translations are accurate and make sense to users. Consider hiring a few additional translators (who didn’t work on the translation process) to complete these quality assurance checks.
And remember, improvements don’t stop at launch. Listen to customer feedback and make adjustments to ensure users are happy with your product.
7. Release product and monitor results
After getting your product to market, it’s important to measure key metrics to understand your success and gain more insights into your new user base.
This involves collecting user feedback, analyzing usage data, and monitoring sales figures.
Examples of localization strategies (good and bad)
Tesco: Failure in the US
In the UK, Tesco is the largest supermarket chain in the country and a member of the “big four”. But over the pond, most Americans will have never heard of the UK’s supermarket giant.
The reason is simple: Tesco’s localization attempt in the USA was a disaster.
In 2007, Tesco launched its US offshoot Fresh & Easy, focusing on small-pack sizes, UK-style ready meals, and relying on self-serve checkouts. In contrast, US consumers prefer to shop in bulk and value good service.
This failure to adapt to the US market ultimately led to the Fresh & Easy brand failing, with all stores closing in 2015.
Learn more about Tesco's US failure
Netflix: Reimagining translation
The streaming giant Netflix started as a US-only service, but now it operates in over 190 countries and offers content tailored to each region.
Its localization strategy covers more than just translating the user interface – it includes localized pricing, regional customer support, and extensive use of subtitles and dubbing in nearly 30 languages.
Netflix also invests in original content for specific markets, like ‘Barbarians’ in Germany and ‘Love Alarm’ in South Korea, ensuring its catalogue appeals to local tastes.
To manage this at scale, Netflix developed its own localization platform and built dedicated teams to oversee language quality and cultural adaptation. This approach has grown a global subscriber base without sacrificing relevance in local markets.
PUBG: The ups and downs of localization
PUBG, the battle royale game with a massive global following, shows how localization can shape a product’s success – and its challenges.
The game is available in nearly 20 languages, with region-specific content like localized characters and audio to reflect cultural expectations, particularly in markets like Japan.
However, PUBG also learned the hard way that cultural missteps can have real consequences. A feature involving idol worship triggered backlash in the Arabic-speaking world, leading to a swift apology and removal of the content.
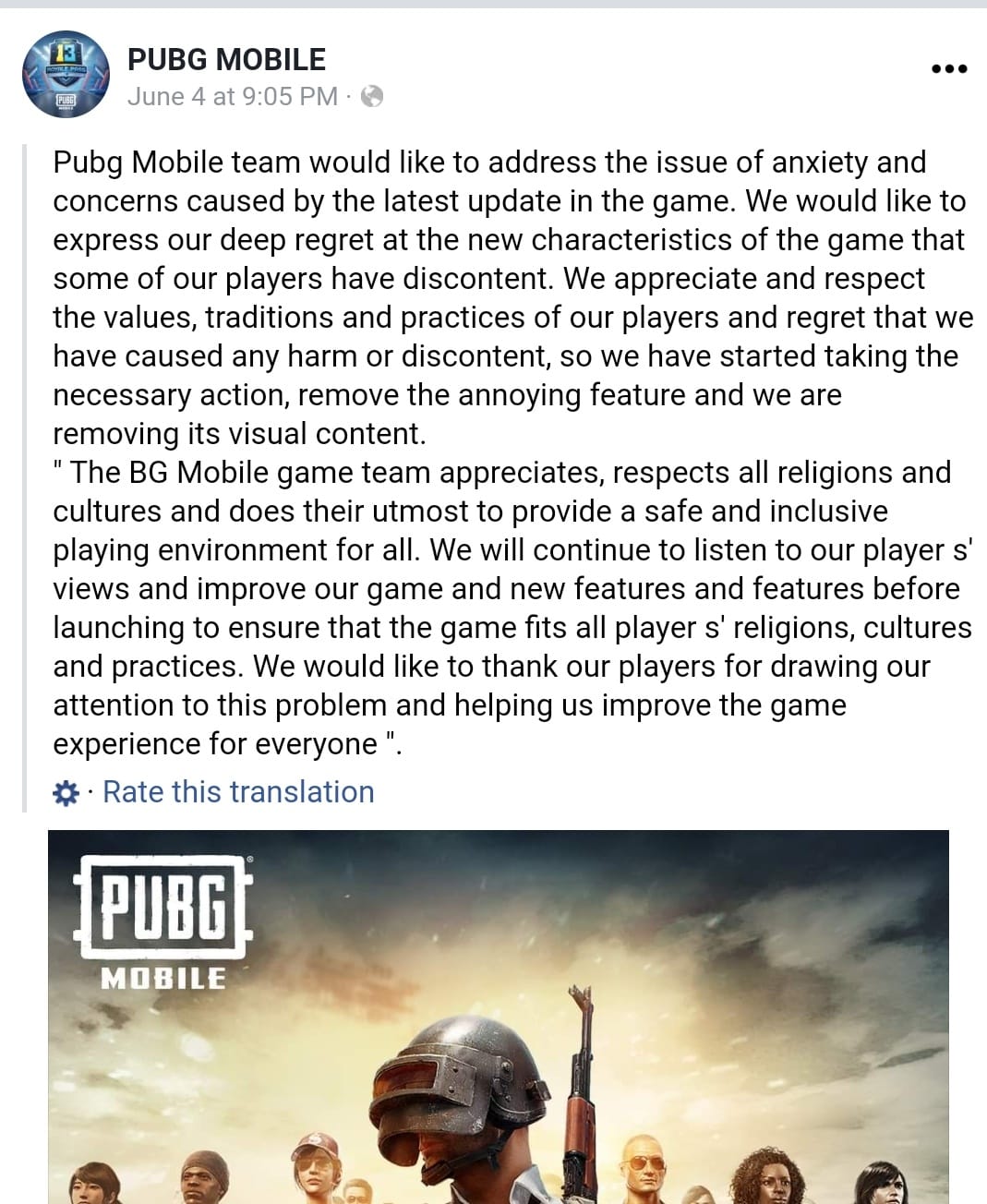
Despite occasional missteps, PUBG’s continued investment in localization (both linguistic and cultural) has helped it stay relevant to a diverse, global player base.
Using product localization tools
To increase efficiency and accuracy during the translation process, many organizations make use of localization tools such as translation management systems (TMS).
These tools allow you to reuse translations, project manage the process, and automate some of the process with AI or machine translation.
Machine-assisted methods for translation (API translation, AI translation, machine translation, and translation memory) have seen an increase of over 20% in just one year, and are now used for 70% of translations, compared to ~59% in 2023.
So, if you want to stay ahead of the competition, it might be time to embrace a powerful localization tool.

Benefits of using a localization tool
Some key benefits of using a localization tool include:
- Improve translation quality with translation memories, glossaries, and additional context.
- Reduce turnaround times through increased efficiency, and gain user feedback quickly.
- Cost savings: reduced time on translation will save you money in man-hours, especially if your agency charges an hourly rate.
- Fast updates directly to your app via over-the-air updates.
- Increase project visibility by tracking completed and pending tasks.
- Easier reporting and analytics as the tool can examine user data and requests for you.
Features to look for
With so many localization software programs on the market, it can be challenging to find one that works for your organization.
To help you narrow it down, here are some of the key features of localization software to look for:
- Translation memory – Stores previously translated content to save time, reduce costs, and ensure consistent phrasing across projects.
- Term bases – Centralizes key terminology for easy reuse, helping maintain consistency and reduce manual oversight.
- Content integration – Connects with your existing tech stack to automate content flow and speed up translation and publishing.
- Project management features – Keeps tasks, deadlines, and team progress organized in one place for better visibility and control.
- Reporting and analytics – Provides insights into translation quality, turnaround times, and team performance to optimize workflows.
- Machine translation capabilities – Enables fast, AI-powered translations – ideal for high-volume or time-sensitive content.
Uncover key localization trends...
Global growth depends on getting localization right.
So we’re bringing you data from 3,000 companies to uncover ways to grow your global user base in 2025.
Ready to simplify localization, reduce costs, and scale globally without losing quality? Get the full eBook today. 👇



 Follow us on LinkedIn
Follow us on LinkedIn









