In the world of product, staying ahead of the competition demands innovation and methodology. Product-led growth (PLG) is one such strategy that has gained immense popularity in recent years.
But what exactly is PLG, and how can it benefit your business? Join us as we explore the concept of product-led growth and its key principles.
What is product-led growth?
Product-led growth is a strategy that focuses on using the product itself as the primary driver of customer acquisition, retention, and expansion. In simpler terms, the product becomes the vehicle for marketing, sales, and customer success. This approach is rooted in the idea that when users experience value from a product, they are more likely to become your loyal customers and advocates, driving organic growth.
Unlike traditional approaches that heavily rely on sales and marketing teams, PLG flips the script. In this model, the product itself takes the lead role in converting prospects into loyal customers.
“Product-led growth is about prioritizing the user experience in everything you do: your product, pricing, marketing, customer engagement and even buying experience.
"An incredible user experience inevitably leads to faster growth, greater customer expansion and best-in-class retention.”
- Kyle Poyar, VP of Market Strategy at Openview
The history of PLG
To truly understand the significance of PLG, we need to delve into its history, tracing its roots and examining the key milestones that have shaped this transformative approach to growth.
The early days
The concept of product-led growth can be traced back to the early days of software development. In the 1980s and 1990s, software companies typically relied on sales teams to drive revenue. Salespeople would engage with potential customers, provide demonstrations, and negotiate contracts. However, this approach had limitations. It was time-consuming, expensive, and often required extensive customization to meet customer needs.
The rise of freemium
One of the first notable shifts towards PLG occurred with the advent of the freemium model. Companies like Skype and Dropbox realized that by offering a basic version of their product for free, they could rapidly acquire a large user base. Users would then organically upgrade to premium versions, driven by the value they experienced during their free usage. This model not only reduced customer acquisition costs but also allowed companies to gather valuable user feedback to improve their products.
The salesforce revolution
Salesforce, founded in 1999, played a pivotal role in advancing the PLG movement. Their customer relationship management (CRM) software was groundbreaking in many ways. Salesforce was among the first to leverage the internet for software distribution and delivery, making it easily accessible to businesses of all sizes.
Their subscription-based pricing model was disruptive, eliminating the need for costly upfront investments. Salesforce's product-centric approach encouraged users to explore and customize the platform independently, promoting self-service and reducing the reliance on sales teams.
The emergence of the App Store ecosystem
The introduction of app stores, notably Apple's App Store in 2008, revolutionized software distribution. This shift enabled software companies to reach a global audience with minimal distribution and marketing costs. Users could discover, download, and use apps independently, creating a seamless user experience. Companies like Slack, Zoom, and Evernote embraced this distribution model, relying on users to find and adopt their products organically.
The role of virality and network effects
Virality and network effects are critical components of PLG. Companies like Facebook, LinkedIn, and Airbnb harnessed the power of network effects, where the value of their platforms increased as more users joined. Invitations, referrals, and social interactions were key drivers of growth. Virality through social sharing and recommendations became integral to acquiring and retaining users.
The mobile app era
The proliferation of smartphones in the late 2000s and early 2010s accelerated the PLG movement. Mobile apps, with their intuitive interfaces and convenient access, created new opportunities for product-led growth. Companies like Uber and Airbnb disrupted entire industries by focusing on user experience and enabling self-service through mobile applications.
The modern PLG landscape
Today, PLG is a dominant growth strategy in the software and technology industry. Companies like Slack, Dropbox, Zoom, and GitHub have achieved remarkable success by putting their products at the center of their growth efforts. These companies prioritize user onboarding, product design, and customer support to create delightful experiences that drive organic adoption and expansion.

What are the key principles of product-led growth?
Understanding PLG principles is huge for businesses seeking sustainable growth and a competitive advantage in today's dynamic marketplace. These principles serve as the foundational building blocks of a successful strategy, allowing companies to create exceptional products. This is done through streamlining user onboarding, employing effective pricing models, engaging users within the product, gathering invaluable user feedback, and making data-informed decisions.
By applying PLG principles, you can shift your focus towards user-centricity, cost-efficiency, and scalability, ultimately fostering higher customer retention rates and organic growth.
In a world where user experience and value delivery reign supreme, grasping the core tenets of PLG is the key to unlocking its potential and achieving your long-term success.
To implement PLG effectively, you need to understand its core principles:
Exceptional product
At the core of PLG is the concept that your product should be top-tier. An exceptional product not only attracts users but also keeps them engaged and satisfied, fostering long-term relationships. This means it should:
Solve real problems: Your product should address genuine pain points or problems that your target audience faces. This understanding comes from thorough market research and user feedback.
User-friendly: An exceptional product is user-friendly, intuitive, and easy to navigate. Users should be able to accomplish tasks with minimal effort.
Continuous improvement: Your product should evolve to meet changing customer needs. This requires a commitment to ongoing development, enhancements, and staying ahead of the competition.
Self-service onboarding
Self-service onboarding is about making it easy for users to get started with your product independently. It reduces friction, allowing users to quickly experience the value of your product. Here's how to achieve it:
Intuitive design: Your product's interface should guide users through the onboarding process with clear and simple design elements. Tooltips, walkthroughs, and interactive tutorials can be effective.
Quick start guides: Provide concise guides or videos that help users understand the core features and how to use them effectively.
Progress tracking: Show users their progress during onboarding. This can motivate them to complete the process and feel a sense of accomplishment.
Freemium model
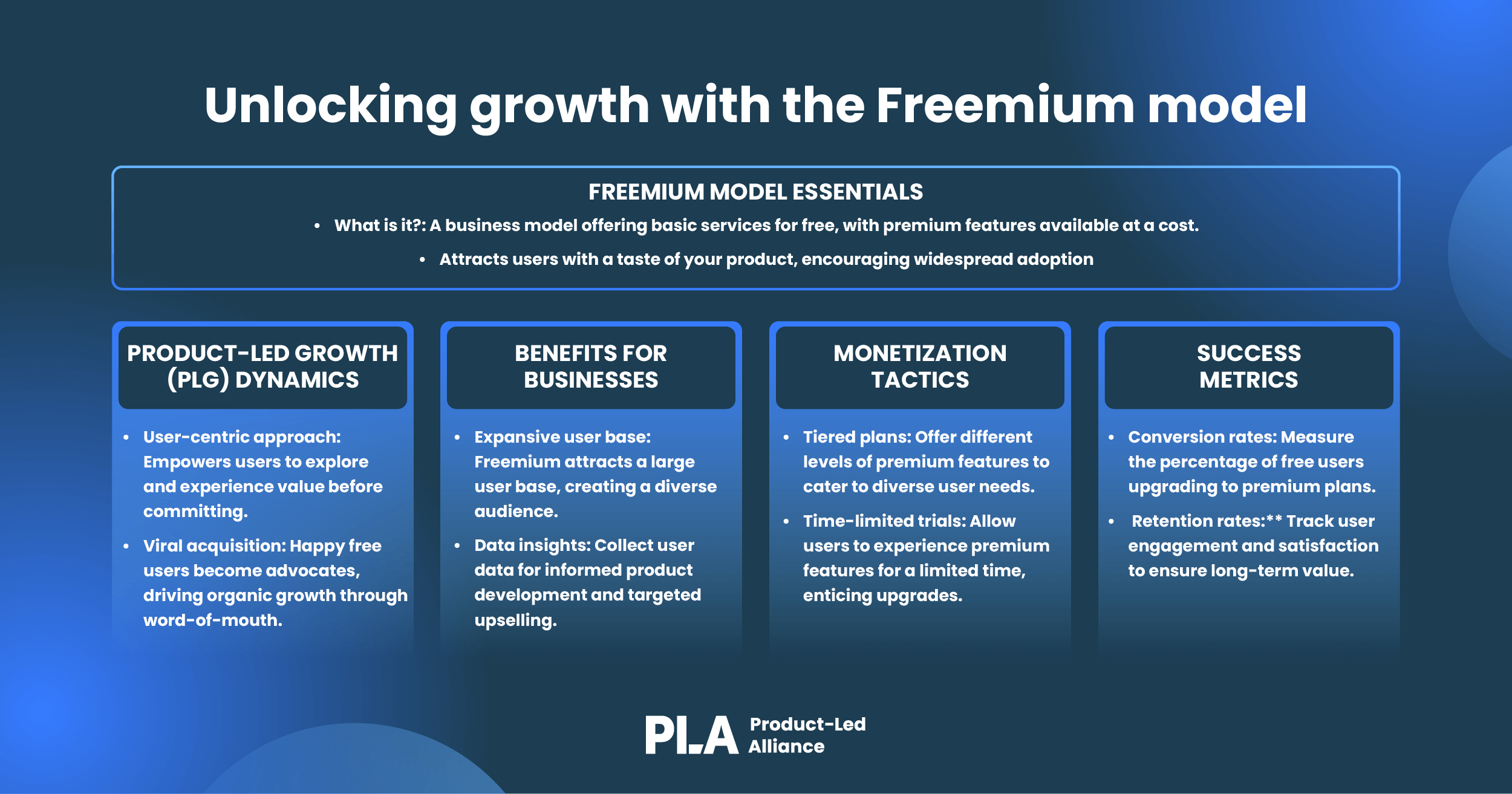
The freemium model involves offering a free version of your product with limited features while reserving advanced or premium features for paid users. It allows users to experience your product before committing financially, reducing the barrier to entry and attracting a wider audience. Here's how to implement it effectively:
Clear differentiation: Clearly define the limitations of the free version and what users can access by upgrading to a paid plan. Transparency builds trust.
Value in the free tier: Ensure that the free version provides real value to users, even if it's limited. This encourages them to stick around and explore premium features.
Upgrade prompts: Strategically prompt users to consider upgrading when they reach the limitations of the free version. Highlight how premium features can benefit them.
In-product marketing
In-product marketing is about leveraging your product interface to educate, engage, and upsell users. It maximizes user engagement and encourages users to explore and unlock the full potential of your product. Strategies include:
Feature announcements: Use in-app notifications to inform users about new features, updates, or improvements. Showcasing value-added features can entice users to explore further.
Tooltips and guides: Implement tooltips and step-by-step guides within the product to help users discover and utilize features effectively.
Personalized recommendations: Use user data to offer personalized product recommendations. This increases relevance and user engagement.
User feedback loop
A user feedback loop involves actively gathering and incorporating user feedback into your product development process. A well-managed user feedback loop demonstrates your commitment to enhancing the user experience and building a product that truly meets their needs. Ways to do this include:
Feedback channels: Establish multiple channels for users to provide feedback, such as surveys, support tickets, and user forums.
Feedback analysis: Analyze user feedback systematically to identify common pain points, feature requests, and issues. Categorize feedback for actionable insights.
Prioritization: Use user feedback to prioritize product improvements and updates. Ensure that you address the most pressing user concerns.
Viral Loops
Viral loops are mechanisms that encourage users to refer others to your product. These leverage your existing user base to drive organic growth, creating a self-sustaining cycle of user acquisition. Strategies for viral loops include:
Referral programs: Incentivize users to refer friends, colleagues, or contacts by offering rewards or discounts for successful referrals.
Social sharing: Make it easy for users to share their positive experiences with your product on social media, email, or other communication channels.
Network effects: Build features that become more valuable as more users join. This naturally encourages users to invite others.
Data-driven decisions
Data-driven decision-making involves using analytics and user behavior data to guide your growth strategy. It helps you make informed choices, ensuring that your product and growth efforts are aligned with user needs and preferences. Try these to boost your decision-making:
Data collection: Implement robust data collection mechanisms to gather insights into user behavior, usage patterns, and conversion rates.
Data analysis: Analyze data to identify trends, anomalies, and areas for improvement. Use A/B testing to evaluate the impact of changes.
Iterative improvements: Continuously iterate and optimize your product and growth strategies based on data insights.
Incorporating these key principles into your PLG strategy can transform your business by putting your product at the forefront of customer acquisition, retention, and expansion efforts.

Sales-led vs. product-led
Product-led growth and product-led sales (PLS) are two distinct approaches in business strategy. PLS emphasizes prioritizing specific users and nurturing leads to close deals. PLS recognizes the importance of personalization and targeted sales efforts to convert potential leads into paying customers.
While both approaches share the goal of driving business growth, PLG emphasizes product adoption and user engagement, while PLS focuses on converting leads into sales through personalized sales strategies.
What are the benefits of product-led growth (PLG)?
PLG has gained widespread recognition and adoption among businesses of all sizes, and for good reason. The benefits it offers can be transformative for organizations, helping them thrive in the ever-evolving business landscape.
- PLG is often more cost-effective than traditional marketing and sales strategies. By leveraging the product as the primary driver of growth, businesses can reduce the expenses associated with outbound marketing, sales teams, and cold outreach. Instead, growth is generated organically through the product itself, making it a budget-friendly approach.
- Prioritization is focused on delivering value to users. When users experience the tangible benefits of a product, they are more likely to become loyal customers. This focus on user satisfaction and ongoing value delivery leads to higher customer retention rates, reducing churn, and the need for constant customer acquisition.
- Emphasis also places users at the center of the growth strategy. This shift in perspective encourages businesses to better understand their customers' needs, preferences, and pain points. By aligning the product with user requirements, PLG fosters stronger customer relationships and brand loyalty.
- PLG is also highly scalable. As more users adopt the product and experience its value, they become advocates who refer others. This word-of-mouth referral system creates a self-sustaining growth loop, allowing businesses to scale rapidly without a linear increase in marketing and sales efforts.
- In a crowded marketplace, a well-executed PLG strategy can set a business apart from competitors. It not only attracts new users but also keeps existing customers engaged and satisfied, making it challenging for rivals to compete on the same level.
- PLG relies on data analytics to inform growth strategies. By tracking key metrics such as user acquisition, activation, retention, and referral rates, businesses gain valuable insights into user behavior. These insights drive iterative improvements and ensure that the product and growth efforts align with user needs and preferences.
How do you become PLG?
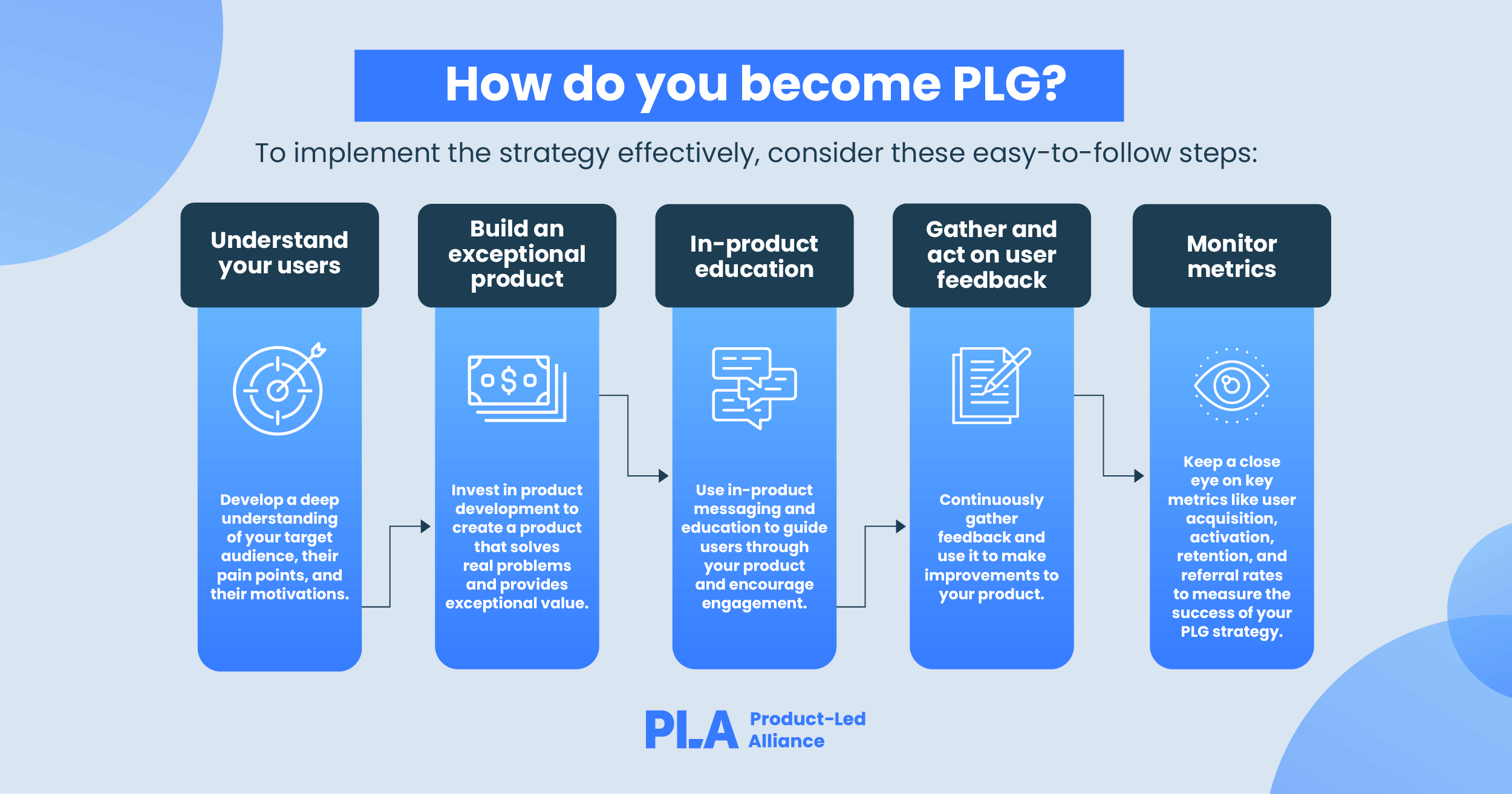
Product-led growth is a powerful strategy that leverages your product to drive sustainable growth. By putting your product at the forefront of your growth efforts and focusing on delivering value to users, you can create a customer-centric, cost-efficient, and highly scalable growth engine for your business. Embracing PLG could be the key to staying competitive and thriving in today's dynamic business landscape.

The significance of measuring metrics
In the thrilling voyage of Product-Led Growth (PLG), metrics act as the compass that guides every decision and steers the course toward success. PLG is all about letting the product lead the charge in driving growth, and measuring the right metrics is the key to unlocking its full potential.
Why is it so crucial to keep a vigilant eye on these numbers? Let's dive into the significance of measuring metrics in PLG.
1. Data-backed decision making
In the realm of PLG, data reigns supreme. Metrics provide you with invaluable insights into how users are engaging with your product, where they're encountering roadblocks, and what aspects of the product resonate the most. Armed with this information, you can make informed decisions about where to allocate resources, which features to prioritize, and how to optimize the user journey. It's like having a treasure map that leads you to the pot of gold – in this case, the pot of growth.
2. Continuous improvement
PLG is an iterative process. It's not about launching a product and sitting back; it's about consistently enhancing the user experience. Metrics allow you to track the impact of your changes and updates. When you see a dip in user engagement or an increase in churn, metrics point you toward the areas that need attention. Just like a seasoned chef adjusting the seasoning to perfection, you can fine-tune your product to deliver maximum value to users.
3. Identifying successes and gaps
Metrics are your spotlight on the stage of growth. They illuminate your successes and highlight the gaps in your strategy. High conversion rates and low churn rates indicate that you're on the right track, while low activation rates and engagement metrics might signal areas that require intervention. Metrics help you celebrate wins and address challenges, ensuring that your PLG journey is a balanced blend of achievements and improvements.
4. Demonstrating ROI and value
When you're steering a ship, it's essential to know that you're headed in the right direction. Metrics enable you to demonstrate the Return on Investment (ROI) and the value that your PLG strategy brings to the table. By showcasing tangible improvements in activation rates, conversion rates, and revenue, you're not just telling a story – you're providing evidence of the impact of your efforts.
5. Alignment and communication
Metrics serve as a common language that aligns teams across the organization. Marketing, sales, product, and customer success teams can all rally around the same set of metrics to gauge the effectiveness of their efforts. It's like a shared roadmap that ensures everyone is on the same page, striving toward a common goal of sustainable growth.
Product-led vs. sales-led vs. market-led
Product-led, sales-led, and market-led approaches are three distinct strategies employed by businesses to drive their growth and achieve success. Each method carries its unique characteristics and implications, catering to various business models and industries.

Sales-led
Sales-led businesses prioritize a more direct approach to selling their products. They employ sales teams, often with inside sales or field sales representatives, to actively engage with potential customers. This strategy is prevalent in industries with complex products, high price points, and customized solutions where a one-on-one sales approach is necessary.
Companies that follow a sales-led strategy invest heavily in sales and marketing efforts to educate, engage, and close deals with customers. Enterprise software, B2B services, and complex industrial solutions are prime examples of industries that rely on sales-led models. While it's resource-intensive, it can yield high-value, long-term clients when executed effectively.
Market-led
Market-led companies, on the other hand, are more focused on understanding the market and customer needs. They place a strong emphasis on research, segmentation, and market analysis to determine the right product-market fit. Market-led strategies involve adapting the product based on market feedback and continuously monitoring market dynamics to stay ahead of competitors.
In market-led approaches, product development aligns closely with market insights, and marketing activities are tailored to resonate with target audiences. This strategy can be observed in consumer goods, healthcare, and even technology markets, where understanding and catering to consumer preferences and market trends are paramount.
While each strategy has its merits, businesses often adopt a hybrid approach, combining elements from different strategies to strike a balance that best suits their objectives, market conditions, and product nature.
Future of product-led
PLG has come a long way, evolving from a disruptive concept into a dominant strategy for business growth. As we peer into the future, it's clear that PLG will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping how companies acquire and retain customers. So, what will the future look like as PLG maintains its hold on the marketplace?
AI and personalization: The future of PLG is intimately linked with the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and personalization. Companies are harnessing AI to understand user behavior, predict needs, and deliver tailored experiences. PLG will increasingly rely on AI-driven product recommendations, in-app guidance, and automated communication to engage users at the right time with the right content. This personalized approach will enhance user satisfaction and drive growth.
Expansion beyond software: While PLG has traditionally been associated with software, its principles are expanding into other industries. SaaS (Software as a Service) companies will remain at the forefront of PLG adoption, but we'll see PLG principles applied to a wider range of products and services. From e-commerce platforms to hardware devices, businesses will increasingly seek ways to empower users to self-serve and experience value independently.
Community-centric growth: Building and nurturing user communities will become central to PLG strategies. Companies will create spaces where users can connect, share insights, and collaborate. These communities will foster user engagement, loyalty, and advocacy. Effective community management will be a key differentiator in PLG's success, as users become not just customers but also brand advocates and contributors.
Omnichannel experiences: The future of PLG will encompass a seamless, omnichannel approach. Users will expect consistent and integrated experiences across web, mobile, social media, email, and more. PLG strategies will incorporate multiple touchpoints, allowing users to engage with the product on their preferred platforms. Omnichannel communication will enable companies to reach users where they are most receptive.
Continuous education and onboarding: User education and onboarding will remain critical components of PLG. Companies will invest in creating intuitive onboarding experiences and educational content that guides users through the product journey. Continuous learning and product improvement will be essential to keeping users engaged and helping them unlock the full potential of the product.
Regulatory and ethical considerations: As PLG continues to evolve, companies will face increasing scrutiny regarding data privacy and ethical practices. Striking the right balance between personalized experiences and user privacy will be a challenge. Companies that prioritize ethical data usage and transparency in their PLG strategies will build trust with users and differentiate themselves in the market.
Conclusion
The world of PLG is a dynamic and transformative landscape where businesses focus on leveraging their products to drive customer acquisition, retention, and expansion. Key takeaways from this exploration of PLG include the shift towards prioritizing user-centricity, cost-efficiency, and scalability.
By applying PLG principles such as offering exceptional products, self-service onboarding, freemium models, in-product marketing, user feedback loops, and viral loops, companies can foster higher customer retention rates and organic growth.
As PLG continues to evolve, it will harness the power of AI and personalization, expand into various industries, build vibrant user communities, offer omnichannel experiences, prioritize continuous education and onboarding, and navigate regulatory and ethical considerations.
The future of PLG promises to be both exciting and challenging as businesses seek to stay competitive and create meaningful user experiences in an ever-changing market environment.



 Follow us on LinkedIn
Follow us on LinkedIn






